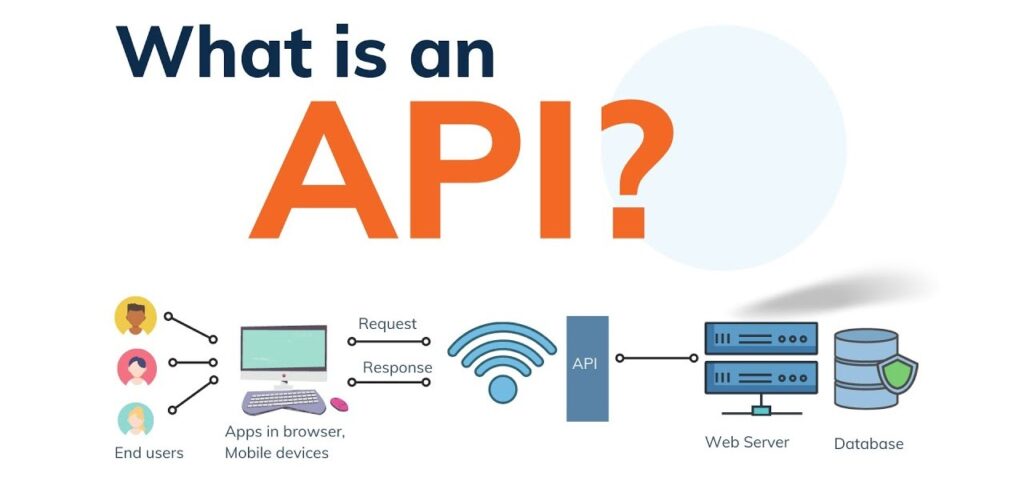
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are the core of smooth communication between different software applications in today’s digital world. In whatever, case it is fetching information from a server or enabling transactions or integrating third party services APIs are the focal point. Nevertheless, reliability, security and performance of these APIs are crucial. It is here that API testing takes center stage.
Let’s examine the different types of API testing to understand how each contributes towards strengthening applications they support.
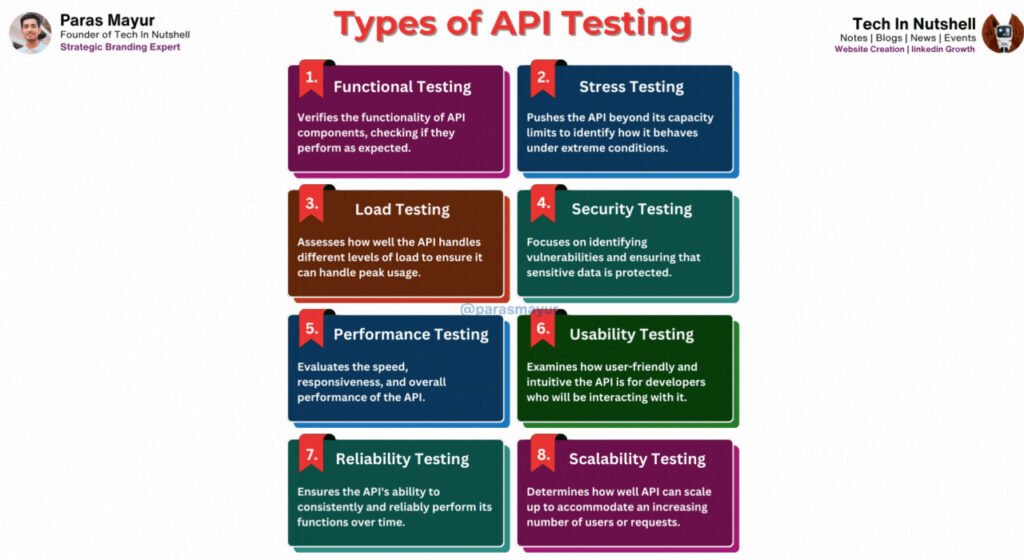
1. Functional Testing
Functional Testing ensures that the functions of API components are as desired. It relates to assessing one-byone functions and return values against any predefined specifications. Through this, developers can ensure that each function works as expected and hence maintain the functionality of API.
2. Stress Testing
Stress Testing takes the API beyond its capacity limits to know how it performs under extreme circumstances. By emulating high traffic loads, spikes in usage or resource constraints the developers can therefore determine possible bottlenecks, performance problems and points of failure.
Also read – Master python from scratch : Guide to programming hero
3. Load Testing
The Load Testing determines the effectiveness of an API when subjected to various levels. With a gradual increase of concurrent users or requests, testers can measure response times, throughput and resource utilization to ensure that the API does not degrade performance at peak usage.
4. Security Testing
Security Testing plays on detecting vulnerabilities and making sure that sensitive data passed through the API is secured. This involves verification of authentication mechanisms, encryption protocols and authorization processes so as to keep out unauthorized accesses or data breaches or other forms of security threats.
5. Performance Testing
Performance Testing measures the speed, response time and general performance of API. Through measuring metrics such as response time, latency and throughput in different conditions testers can enhance the API for efficiency and reliability thereby making it easy to use.
6. Usability Testing
Usability Testing looks at the ease of use and intuitiveness of an API for developers using it. This encompasses assessing the documentation, error messages and integration ease to ascertain that developers could understand and apply the API without facing any challenges.
7. Reliability Testing
Reliability Testing guarantees the API’s ability to perform its functions repeatedly over time. Through continuous testing and by tracking for errors, crashes or memory leaks the developers can detect any problem that may affect the reliability of availability of API.
8. Scalability Testing
Scalability Testing identifies the ability of an API to scale up as a result of handling more users or requests. Through the simulation of growth scenarios and resource monitoring, developers can improve architecture and infrastructure for API to accommodate scalability requirements efficiently.
Conclusively, API testing is an integral part of software development that guarantees the integrity, safety and efficiency in APIs. Using various API testing methodologies, developers can detect and fix problems at the early stages of application development life cycle that results in high-quality applications with resilience to failure free from user dissatisfaction.