Among those just entering the world of databases, the term “DBMS architectures” is likely to arise. With some practice, it won’t seem as daunting as initially thought. Understanding how they work, we shall dissect DBMS structures throughout this essay. Starting point: for any one interested (student, entrepreneur, etc.), here we go!
DBMS: What Is It?
Comparable to a digital library’s keeper, a DBMS manages databases. This device enables efficient management, saving, and recovery of data. Data management becomes more streamlined when viewed as software.
Why Are DBMS Architectures Necessary?
Let’s now discuss DBMS architectures. A range of possibilities exists within DBMS configuration choices. Just as there are various home design choices, so too are there multiple approaches for constructing a DBMS.
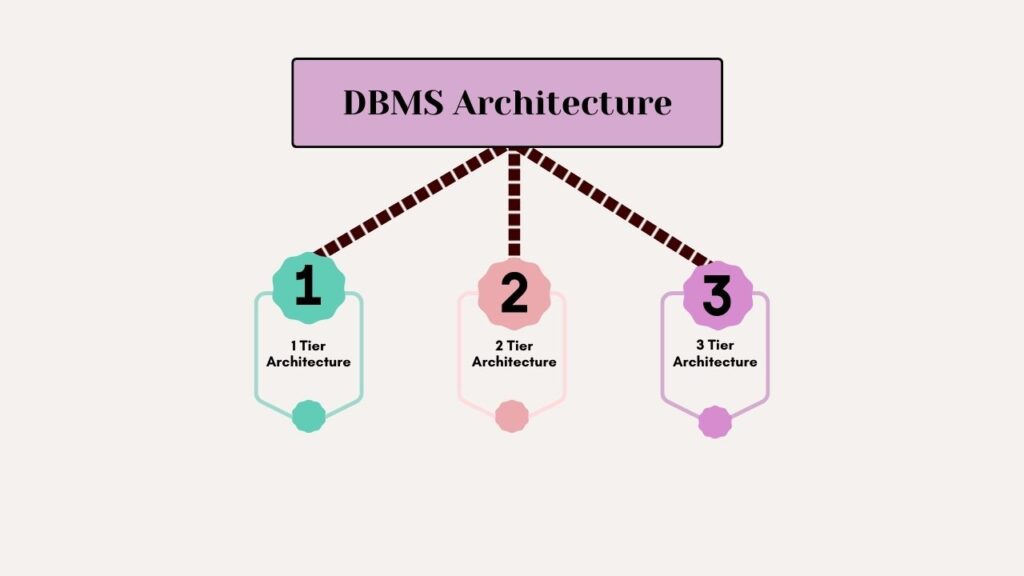
DBMS architecture types
1. Single-tier Architecture (Stand-alone): Imagine a single librarian presiding over every book, all in one space. Same computer housing, the database and DBMS software have their home.
– A small-scale application, personal databases excel at these types of tasks.
2. Double-Tier Architecture : Think of it like this a dual-layered structure comprising numerous librarians and one central information desk.
– In this case, the database management system (DBMS) is divided into two components: A server functions as the central hub for data storage and processing, while clients access it remotely.
– A standard feature in commercial settings, this configuration enables various people to see shared information.
3. A three-tiered architecture: A library complete with librarian support and reserved book areas can be envisioned.
– There are three levels in this configuration: Through the display layer, you interact with the database; via the application layer, your requests are handled; and within the database layer lies the information itself.
– Online application benefits from separation of user interface (UI) from data storage by…
4. “N-tier architecture”: A comprehensive library featuring separate areas devoted to distinct types of writing.
– Above the standard three-level structure lies the option to incorporate extra tiers according to demand.
– Its versatility makes it suitable for massive endeavors requiring nuanced solutions.
Also read – How AI is Transforming Data-Driven Marketing
Conclusion
Several DBMS architecture choices exist that cater to various data storage and retrieval needs. Individual tastes guide choices, just like choosing home designs according to household needs.
By comprehending different design approaches, selecting the ideal DBMS solution grows simpler regardless of how extensive one’s dataset happens to be.